The Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training Study (Sprint) evaluates the use of high intensity, low volume exercise training to minimize loss of muscle, bone, and cardiovascular function in International Space Station (ISS) crew members during long-duration missions.
The objective is to evaluate a new exercise prescription using new exercise hardware on ISS. The new Integrated Resistance and Aerobic Training Study (Sprint) protocol uses an evidence based approach to develop a higher intensity, lower duration exercise program utilizing ISS exercise hardware: the Advanced Resistance Exercise Device (ARED) and a second generation treadmill, Combined Operational Load Bearing External Resistance Treadmill (COLBERT). Accordingly, Sprint differs from standard care primarily on the increased intensity and decreased total exercise time. The effectiveness of Sprint is determined by comparison of pre- and post-flight measurements of muscle, cardiovascular and bone health against two other groups. The comparison groups include crew members who perform the standard care exercise prescription utilizing the newly designed exercise hardware (ARED and COLBERT), and a historic data set of those who used a standard care exercise prescription using the old exercise hardware. Upon completion of this study, investigators expect to provide an integrated resistance and aerobic exercise training protocol capable of maintaining muscle, bone and cardiovascular health while reducing total exercise time over 180 days of spaceflight. This is likely to provide invaluable information in support of the long-term goal of protecting human fitness for even longer space exploration missions.
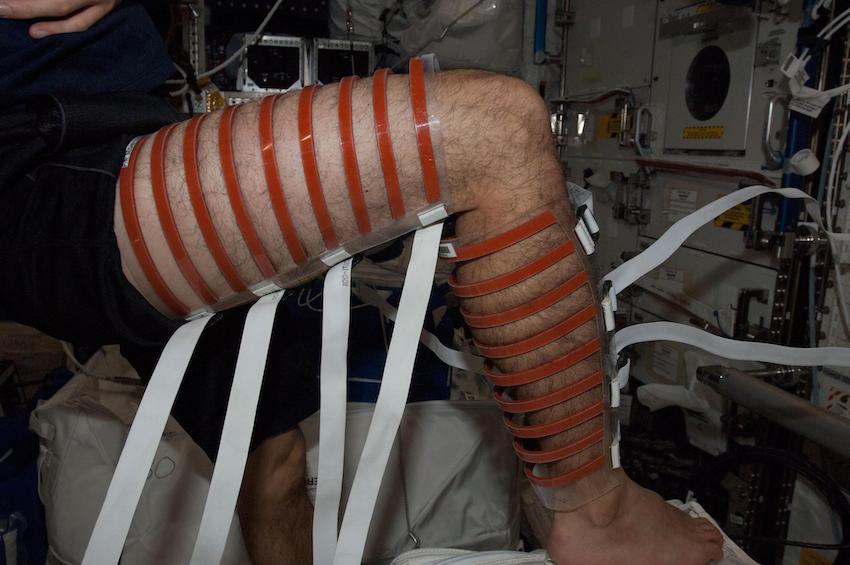
Subjects will be tested pre and post flight for a thorough analysis of muscle, bone and cardiovascular fitness. Tests include: Muscle Performance Measures, MRI scans along the entire leg to characterize spaceflight-induced change in muscle Cross Sectional Area (CSA), ultrasound scans of the thigh and calf to be compared to the MRI results in an attempt to validate the use of Ultrasound in evaluating muscle CSA, Maximal Aerobic Capacity (VO2max), a muscle biopsy, and bone testing including the current standard Dual X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) medical requirement and Quantitative Computed Tomography (QCT).
Crewmembers will use the ARED and T2 during their normal gym time for several weeks prior to launch to become familiar with the hardware and iRAT prescription. In-flight monitoring of training loads on ARED and T2 will be evaluated as assessment of muscle function. Cardiovascular fitness assessment will include a monthly measurement of VO2max. Muscle response in-flight will be measured via Ultrasound scans during the duration of the subject’s mission. Subjects will perform the new iRAT exercise prescription 6 days per week in-flight, beginning as early as possible. Control subjects will only perform the BDC portion of the protocol (i.e., no inflight activities).
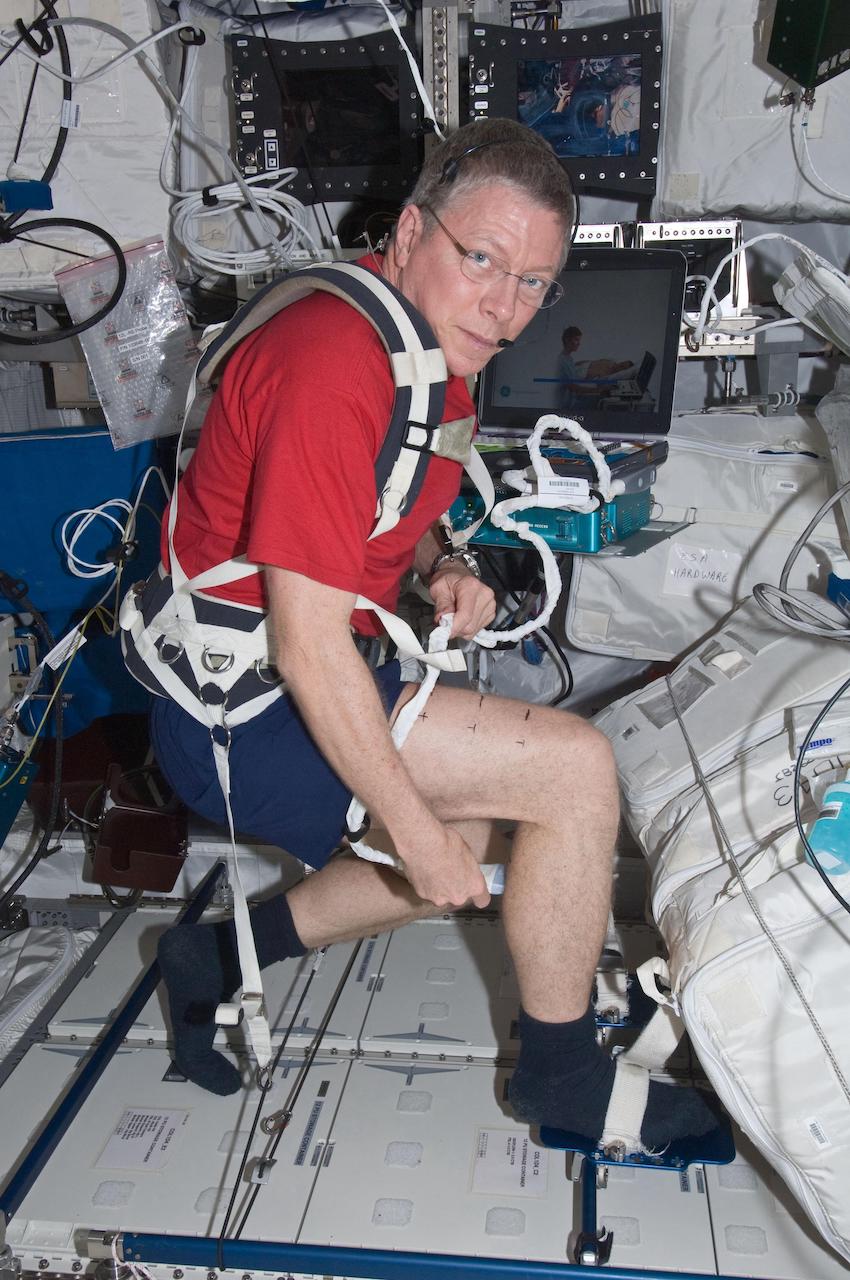

NASA astronaut Mike Fossum, Expedition 29 commander, performs a SPRINT leg muscle self scan in the Columbus laboratory of the International Space Station (Photo: NASA)